

#Find explicit formula for arithmetic sequence professional#
Tutors, instructors, experts, educators, and other professionals on the platform are independent contractors, who use their own styles, methods, and materials and create their own lesson plans based upon their experience, professional judgment, and the learners with whom they engage. Varsity Tutors connects learners with a variety of experts and professionals. Varsity Tutors does not have affiliation with universities mentioned on its website.

Media outlet trademarks are owned by the respective media outlets and are not affiliated with Varsity Tutors.Īward-Winning claim based on CBS Local and Houston Press awards. In contrast, an explicit formula directly calculates each term in the sequence and quickly finds a specific term.īoth formulas, along with summation techniques, are invaluable to the study of counting and recurrence relations.Names of standardized tests are owned by the trademark holders and are not affiliated with Varsity Tutors LLC.Ĥ.9/5.0 Satisfaction Rating based upon cumulative historical session ratings through 12/31/20. How do you use explicit formulas to find terms of arithmetic sequences If this had been a recursive formula. Throughout this video, we will see how a recursive formula calculates each term based on the previous term’s value, so it takes a bit more effort to generate the sequence. Find the 50th term of the sequence given below. We want to remind ourselves of some important sequences and summations from Precalculus, such as Arithmetic and Geometric sequences and series, that will help us discover these patterns. And it’s in these patterns that we can discover the properties of recursively defined and explicitly defined sequences. by 2 be -13 Select the correct answer below: O b 7 - 50 O 04-12-10 O b. What we will notice is that patterns start to pop-up as we write out terms of our sequences. Find the explicit formula for the arithmetic sequence bn given the information below.
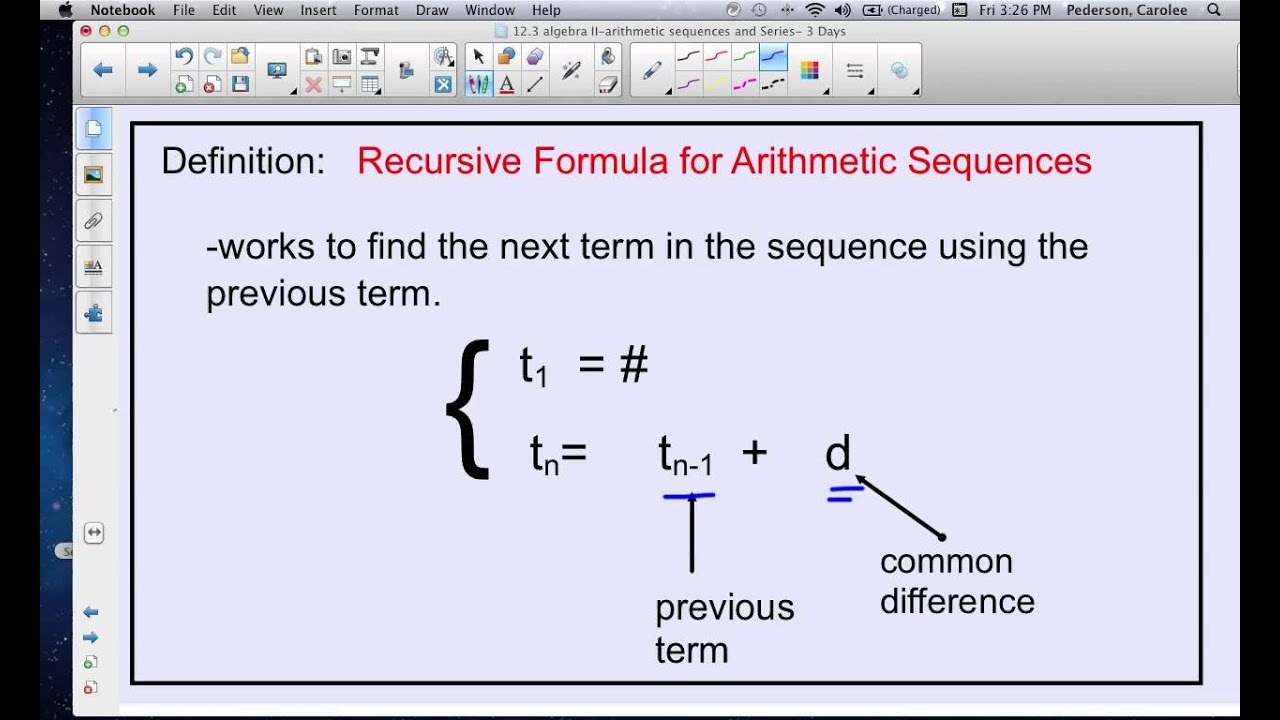
All this means is that each term in the sequence can be calculated directly, without knowing the previous term’s value. So now, let’s turn our attention to defining sequence explicitly or generally. It is represented by the formula an a(n-1) + a(n-2), where a1 1 and a2 1. Isn’t it amazing to think that math can be observed all around us?īut, sometimes using a recursive formula can be a bit tedious, as we continually must rely on the preceding terms in order to generate the next. A Fibonacci sequence is a sequence of numbers in which each term is the sum of the previous two terms. b 2 b -13 This problem has been solved Youll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Each term is the sum of the previous term and. Find the explicit formula for the arithmetic sequence bn given the information below. In fact, the flowering of a sunflower, the shape of galaxies and hurricanes, the arrangements of leaves on plant stems, and even molecular DNA all follow the Fibonacci sequence which when each number in the sequence is drawn as a rectangular width creates a spiral. A recursive formula allows us to find any term of an arithmetic sequence using a function of the preceding term. For example, 13 is the sum of 5 and 8 which are the two preceding terms. Now that you have the explicit formula, find the 100th term of this sequence. (Opens a modal) Converting recursive & explicit forms of arithmetic sequences. (Opens a modal) Arithmetic sequence problem. (Opens a modal) Explicit formulas for arithmetic sequences. Notice that each number in the sequence is the sum of the two numbers that precede it. explicit formula: an 10 + 5 (n - 1) 10 + 5n - 5 5 + 5n or 5n + 5. Recursive formulas for arithmetic sequences. To find your common difference, find 13- (-5). Since you have b (1), you look at what your first term is.
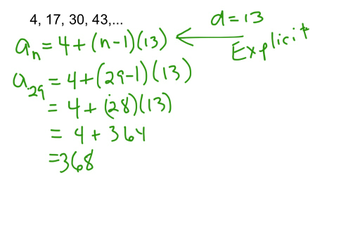
The variable d represents the common difference and the a is whatever number of the term you are using. And the most classic recursive formula is the Fibonacci sequence. The formula for explicit formula is b (n)b (1)+d (n-1). Staircase Analogy Recursive Formulas For SequencesĪlright, so as we’ve just noted, a recursive sequence is a sequence in which terms are defined using one or more previous terms along with an initial condition. The explicit formula for the given arithmetic sequence is a 81 + (n-1)(-27).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
